Uses and applications
With the use of edge protection when handling equipment and machine parts made of sheet metal profiles, the risk of cuts or abrasions is reduced to a minimum. In the process, in these applications the profiles provide a visual “decorative effect.” Other application possibilities include cable and tube laying, where openings and edges of divider plates need to be bypassed. This provides reliable protection from flaking or worn-down cables and tubes.
In general, using edge protection profiles can reduce the need for further treatment such as burring and chamfering of cut or laser-cut metal sheets.
Edge protection seal profiles provide the same benefits as edge protection profiles. However they are recommended for use in cases where doors, covers and hatches require additional sealing in order to prevent the emission of dust, warm air or noise; for example, or in order to prevent water spray from entering.
Structure
Edge protection profiles consist of an extruded clamping profile which forms the base of the structure and is used on the edge of sheet metal in order to affix the edge protection profile.
In order to increase the clamping force, the clamping profile is strengthened through a reinforcement, preventing the profile from detaching itself after assembly.
The clamp insert is available as a steel clamping band or as a steel wire polyester clamping band. Steel clamping bands have a higher clamping effect, while steel wire clamping bands allow a smaller assembly radius, also enabling a more even alignment of the edges.
The seal profile is affixed to the top or the side of the clamping profile and is significantly “softer.” It can be made from the basic material of the clamping profile but it can also be made from particular materials for specific applications. In order to attain optimum sealing, the seal profile needs to be prestressed and/or formed to enable it to adapt precisely to the countersurface.
The sealing lips in the interior of the clamping profile ensure the sealing of the edge protection seal profile with the edge of the sheet.

Assembly
Side cutters and scissors that are suitable for cutting the metal clamping insert can be used to align the profiles. Any end parts of the clamp insert that protrude from the cutting area should be removed in order to prevent injuries. The profile ends and cants can be subsequently sealed and/or glued as required.
The mounting of the the profiles to the edges is secured via the clamp insert. Glue or other adhesives are not usually required.
Profiles can generally be assembled by applying pressure by hand. If necessary, the profile can additionally be secured by lightly applying a soft-face hammer.
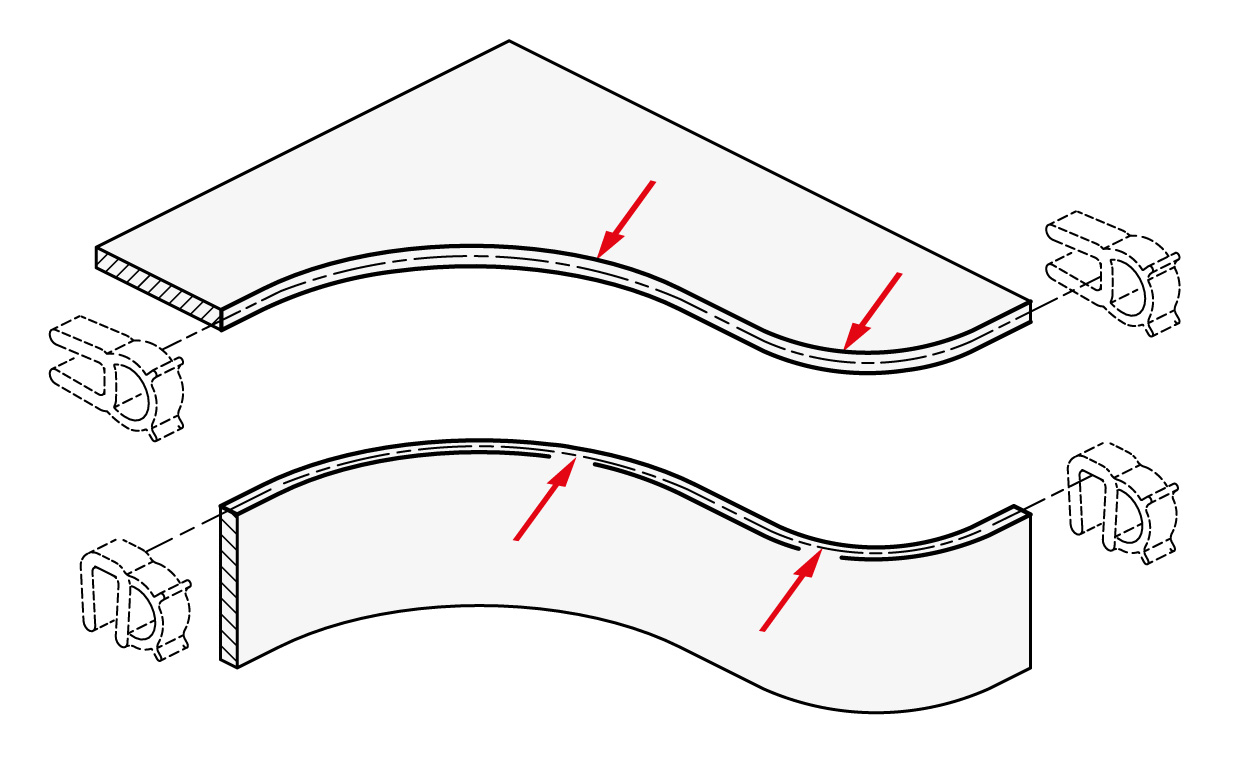
Minimum placement radii
In order to ensure a consistent seal for the profile and to prevent the profile from deta-ching, placement should not be set below the minimum radii. This also makes the profile assembly easier.
The radii are listed on the corresponding standard sheets and should be used as a guideline. Depending on the direction of application, a distinction is made between cut or curved radii, in other words, interior or exterior seal profiles.
Shaping
Ideally, edge protection seal profiles should maintain a deformation x of approximately 30 - 50% of the maximum value in order to ensure reliable sealing.
Deformation of over 50% can impair seal tightness and reduce the resilience of the sealing material due to plastic deformation.

Basic materials, characteristics
Profiles can be made from various basic materials depending on the application. The table to the right summarizes the general characteristics to facilitate the choice.
Due to the multitude of chemicals, solvents etc. exact specifications are not possible, as basic materials that are fundamentally unstable can be durable in combination with specific materials and vice versa. Concentration, temperature and exposure time also play a crucial role. The customer is advised to test resistance when combining respective materials in contact with one another.
| Characteristics | PVC | NBR | EPDM |
| Operational temperature min. | -40 °C | -30 °C | -40 °C |
| Operational temperature max. | +70 °C | +100 °C | +100 °C |
| Abrasion resistance / Wear resistance | + | + | + |
| Deformation resistance | o | + | + |
| Resistant to: * | |||
| UV light / weather exposure | + | - | + |
| Chemicals | + | - | + |
| Oil, greases | o | + | - |
| Fuels | o | + | - |
| Acids | + | o | + |
| Alkalines | o | + | + |
| Solvents | o | o | o |
| Alcohol | o | o | + |
* + resistant, o conditionally resistant, – non-resistant
UL certification (Seal profiles as EPDM)
UL (Underwriters Laboratories) is an independent global company operating in safety science, similar to TÜV in Germany. Their testing is required as a priority in the US-American market.
The GN 2180 edge protection seal profiles made of EPDM have a “UL-recognized component” mark. This states that the profiles can be used as components in finished products which are also intended for UL-certified use.
For customers and companies, the need for these types of certification is becoming increasingly important, as it guarantees high quality, reliable processing, and long durability, as well as reliable product safety.

